HUMAN CELL:
This my second topic in which I'm describing about Human Cell. This is just a basic introduction and if you want you can add up to this . I'm just posting slides and the brief explanation of these slides are being discussed in both Tamil and English in my YouTube channel "Nursing Abstract". You can watch out for more videos and post in upcoming days. If you have any queries and suggestions kindly post in the comments section below.my YouTube channel link
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCZrabu-CtMa5AEexu1j2GNw
My Tamil video link: https://youtu.be/Rmz8c7B9tbw
My English video link: https://youtu.be/iW0hBbRGMas
INTRODUCTION:
Cell is the body’s smallest functional unit.
Cells are grouped together to form tissues (example :blood ,muscle ,bone etc..).
Different tissues are grouped together to form organs (example : eyes ,stomach etc…)
Organs are grouped together to form systems (example: digestive system etc..)
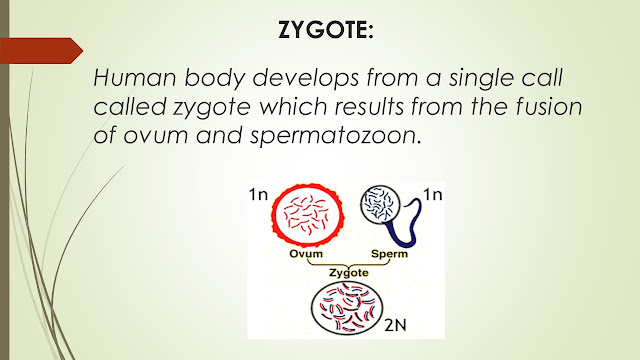
ZYGOTE:
Human body develops from a single cell called zygote which results from the fusion of ovum and spermatozoon.
CYTOSOL:
Cell consists of plasma membrane enclosing a number of organelles suspended in a watery fluid called cytosol.
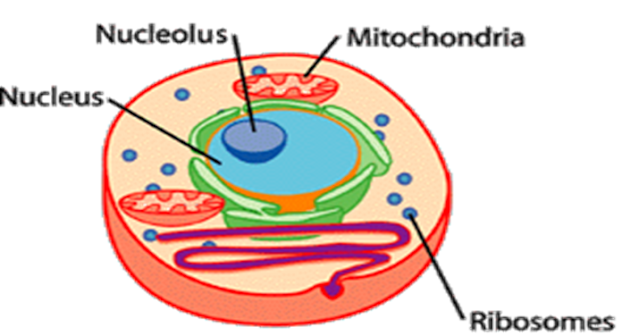
Human cell:
ORGANELLS IN A CELL:
It includes
1. The Nucleus
2. Mitochondria
3. Ribosomes
4. Endoplasmic reticulum (smooth & rough)
5. Golgi apparatus
6. Lysosomes
7. Cytoskeleton
8. Cytoplasm(cytosol &organelles excluding nucleus).
I. PLASMA MEMBRANE:
The plasma membrane consists of 2 layers of phospholipids with proteins and sugar embedded in them. In addition lipid cholesterol is also present. The phospholipid molecule have a head and a tail. THE HEAD is electrically charged and hydrophilic (water loving). THE TAIL has no charge .
They are arranged in a sandwich layer with the hydrophilic head on outer and the hydrophobic tail on inner (water repelling layer).
These differences influence the transfer of substances across the membrane.
II. NUCLEUS:
It is the largest organelle contained within the nuclear envelope.
It has tiny pores through which some substances pass between it and the cytoplasm.
It contains genetic material which is in the form of DNA.
In non dividing cell DNA is in the form of fine network of thread called chromatin .
When the cell prepares to divide the chromatin structures form a distinct structures called chromosomes.
RNA is found in nucleus which are involved in protein synthesis.
Roughly spherical shaped structure called nucleolus which is involved in the synthesis and assembly of component of ribosomes.
III.MITOCHONDRIA:
It is membranous & sausage shaped structure in the cytoplasm
It is also called as POWER HOUSE OF CELL.
It is important in aerobic respiration by which it processes chemical energy is made available in the cell.
It is in the form of ATP which releases energy when the cell breaks it down.
The most active cell type have greatest number of mitochondria (example : liver, muscle, spermatozoa.
IV.RIBOSOMES:
They are tiny granules composed of RNA and proteins.
They synthesize proteins from
amino acid using RNA as a template.
They are in free units or in small clusters in the cytoplasm.
They make use of protein within the cell.
They are found in the nuclear envelope outer surface & rough endoplasmic reticulum where they manufacture proteins for export from the cell.
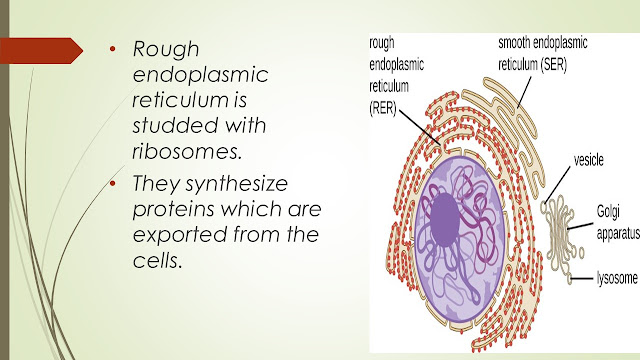
V.ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM:
They are interconnecting membranous canal.
There are smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum.
SMOOTH ER synthesize lipids and steroid hormones.
It is associated with detoxification of some drugs.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum is studded with ribosomes.
They synthesize proteins which are exported from the cells.
IV.GOLGI APPARATUS:
They are closely folded flattened membranous sacs.
Proteins move from ER to golgi apparatus where they are packed into membrane bound vesicles.
Vesicles are stored and when needed they are moved to plasma membrane and fuse with it.
VII. LYSOSOMES:
Lysosomes are small membranous vesicles.
They contain a variety of enzymes involved in breaking down fragments of organelles and larger molecules (eg. RNA ,DNA , carbohydrate ,protein) inside the cell into smaller particles that are either recycled or extruded from the cell as waste material.
Lysosomes in WBC contain enzymes that digest foreign material such as microbes .it is involved in the process of phagocytosis.
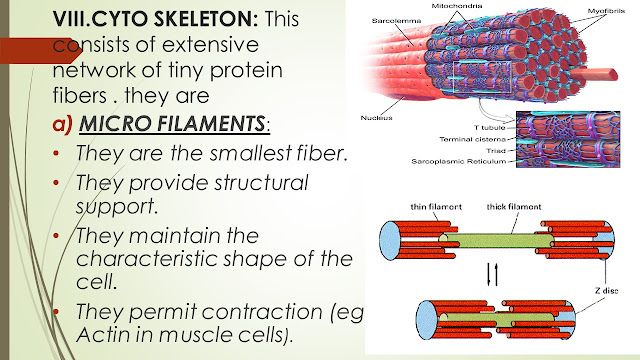
VIII.CYTO SKELETON: This consists of extensive network of tiny protein fibers . they are
MICRO FILAMENTS:
They are the smallest fiber.
They provide structural support.
They maintain the characteristic shape of the cell.
They permit contraction (eg. Actin in muscle cells).
b) MICRO TUBULES:
They are larger contractile protein fibers that are involved in the movement of
Organelles within the cell
Chromosome during cell division
Cell extension.
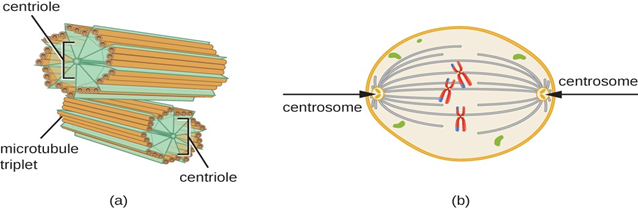
c) CENTROSOME:
It directs organization of microtubules within the cell.
It consists of a pair of centrioles (small clusters of microtubules).
It plays an important role in cell division.
d) CELL EXTENSION:
these projects from plasma membrane into some types of cells .Main component is microtubules which allows movement. They include
MICROVILLI: They are tiny projections that contain microfilaments.
They cover the exposed surface of certain types of cells (eg: absorptive cells that line the small intestine.)
By this structure it maximizes the absorption of nutrients from the small intestine.
CILIA:
They are microscopic hair like projections containing microtubules that lie along the free border of the cell.
They beat in unison, moving of the substance along the surface (eg: mucus upward in respiratory tract).
FLAGELLA:
They are single long whip like projections containing microtubules which from the tail of spermatozoa.
That propel them through the female reproductive tract.