Hey guys. In today's topic we are going to discuss about " THE MUSCLE TISSUE". Tissues are a group of cells with similar functions and function together as a unit. There are mainly four types of tissue, they are The Epithelial tissue, The Connective tissue, The Muscle tissue and The Nervous tissue.
So far we have discussed about the epithelial tissue and connective tissue and today we are going to discuss on 'THE MUSCLE TISSUE'. I have prepared slides and Using the slides I'm posting videos in YouTube in both English and Tamil. check out for a brief explanation. If you have any suggestions kindly post in the comments section below.
Channel Link:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCZrabu-CtMa5AEexu1j2GNw
English video:https://youtu.be/Lt8LHpARJRY
Tamil video:https://youtu.be/6wC7S0EKZXg
TYPES OF TISSUES:
There are 4 main types of tissues each with subtypes .they are
1.EPITHELIAL TISSUE OR
EPITHELIUM.
2.CONNECTIVE TISSUE.
3.MUSCLE TISSUE.
4.NERVOUS TISSUE
3. MUSCLE TISSUE:
This tissue is able to contract and relax, providing movement within the body.
Muscle contraction requires a blood supply that will provide sufficient oxygen, calcium and nutrients and remove waste products.
There are 3 types of specialized contractile cells ,also known as fibers :
1.skeletal muscle
2. smooth muscle.
3.cardiac muscle.
SKELETAL MUSCLE:
This muscles moves the bones(skeleton) and it is under voluntary conscious control.
The diaphragm is made from this type of muscle to accommodate a degree of voluntary control in breathing.
These fibers are cylindrical, contain several nuclei and can be upto 35cm long.
Skeletal muscle contraction is stimulated by motor nerve impulses originating in the brain or spinal cord ending in the neuro muscular junction.
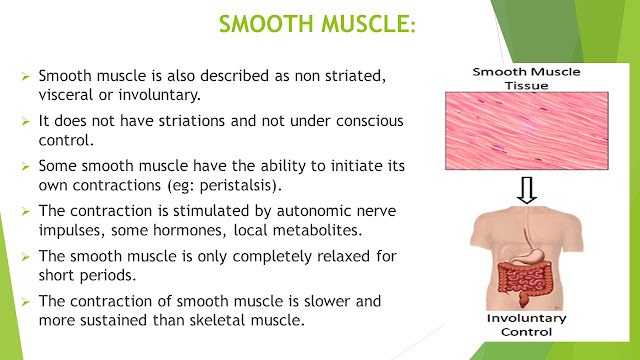
SMOOTH MUSCLE:
Smooth muscle is also described as non striated, visceral or involuntary.
It does not have striations and not under conscious control.
Some smooth muscle have the ability to initiate its own contractions (eg: peristalsis).
The contraction is stimulated by autonomic nerve impulses, some hormones, local metabolites.
The smooth muscle is only completely relaxed for short periods.
The contraction of smooth muscle is slower and more sustained than skeletal muscle.
It is found in the walls of hollow organs:
1. Regulating the diameter of blood vessels and parts of respiratory tract.
2. Propelling contents along eg: the uterus, alimentary tract and ducts of glands.
3. Expelling contents of urinary bladder and uterus.
When examined under a microscope, the cells appear like a spindle shaped with one central nucleus.
Bundles of fibers form sheets of muscle, which are found in the walls of above structures.
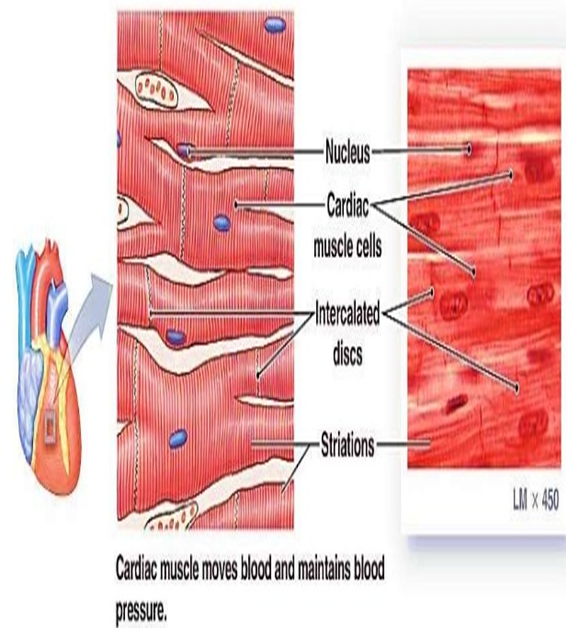
CARDIAC MUSCLE:
This is found only in heart wall.
It is not under conscious control.
Under microscope cross strips(striations) characteristic of skeletal muscle can be seen.
Each fiber (cell) has a nucleus and one or more branches.
The ends of the cells and their branches are in very close contact with the end and branches of the adjacent cells.
Microscopically these joints or intercalated discs , appears as lines that are thicker and darker than the ordinary cross stripes.
When the heart contracts as a wave of contraction spreads from one cell to cell across the intercalated discs, which mean than the cardiac muscle fibers do not need to be stimulated individually.
The heart has a natural pace maker system ie: SA Node ,which means that it beats in a coordinated manner without external nerve stimulation , the rate at which it beats is by autonomic nerve impulse, some hormones , local metabolites and other substances.
















Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for supporting me . ;I'll try my level best to give the accurate and updated knowledge in all the topics . please visit my YouTube channel named Nursing Abstract ; for viewing a brief explanation in both Tamil and English . see you again in my next post.