Connective tissue is the tissue which connects the other tissues. It also separates and supports all other types of tissues in the body.
Major functions of connective tissue include:
1) binding and supporting
2) protecting
3) insulating
4) storing reserve fuel
5) transporting substances within the body.
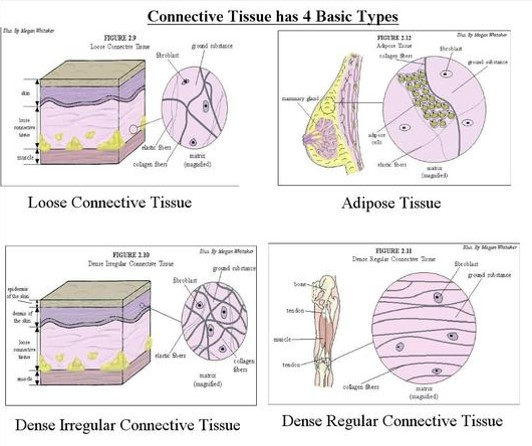
TYPES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE:
- Loose (areolar) connective tissue
- Adipose tissue
- White adipose tissue
- Brown adipose tissue
- Reticular tissue
- Dense connective tissue
- Fibrous tissue
- Elastic tissue
- Hyaline cartilage,
- Fibrocartilage ,
- Elastic cartilage
- Bone
CELLS IN CONNECTIVE TISSUE:
LOOSE {AREOLAR} CONNECTIVE TISSUE:
Areolar connective tissue holds organs in place and it also attaches the epithelial tissue to the other underlying tissues.
It also serves as a reservoir of water and salts for surrounding tissues.
Almost all cells obtain their nutrients from and release their wastes into areolar connective tissue
These tissues are widely distributed and serve as a universal packing material between other tissues.
The functions of areolar connective tissue is to support and to bind the other tissues.
It also helps in defending against infection.
The areolar connective tissue is the most generalized type of connective tissue.
The matrix is semisolid with many fibroblasts , fat cells(adipocytes),mast cells , macrophages widely separated by elastic and collagen fibers.
It is found in every part of the body and it provides elasticity and tensile strength.
It connects and supports other tissues
eg :under the skin , between muscles , supporting blood vessels and nerves , in the alimentary canal.
ADIPOSE TISSUE:
Adipose tissue consists of fat cells (adipocytes),containing large fat globules , in a matrix of areolar tissue. There are 2 types: white and brown.
WHITE ADIPOSE TISSUE: this makes up 20-25% of body weight in adults with a normal BMI; more is present in obesity and less in those who are under weight.
Adipose tissue secretes the hormone leptin.
The kidneys and eye balls are supported by adipose tissue , which is also found between muscle fibers and under the skin , where it act as a thermal insulator and energy store.
BROWN ADIPOSE TISSUE:
This is present in newborn.
It has more extensive capillary network than white adipose tissue.
When brown tissue is metabolized, it produces less energy and considerably more heat than other fat , contributing to the maintenance of body temperature.
Some times small amounts are present in adults.
RETICULAR TISSUE:
Reticular tissue has a semisolid matrix with fine branching reticulin fibers.
It contains reticulin cells and white blood cells (monocytes &lymphocytes).
Reticular tissue is found in lymph nodes and all organs of the lymphatic system.
DENSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE:
The dense connective tissue contains more fibers and fewer cells than the loose connective tissue.
FIBROUS TISSUE:
This tissue is mainly made up of closely packed bundles of collagen fibers with very little matrix.
Fibrocytes (old and inactive fibroblasts) are few in number and lie in rows between the bundles of fibers.
Fibrous tissue is found in
Forming ligaments ,which binds bones together.
As an outer protective covering for bone, called periosteum.
As an outer protective covering for some organs.eg: the kidneys , lymph nodes, brain.
Forming muscle sheaths called muscle fascia, which extends beyond the muscle to become the tendon that attaches the muscle to the bone.
ELASTIC TISSUE:
Elastic tissue is capable of considerable recoil and extension.
There are few cells and the matrix consists mainly of masses of elastic fibers secreted by fibroblast.
It is found in organs where alteration of shape and stretching is required.
Eg: large blood vessels ,trachea ,bronchi ,lungs .
CARTILAGE:
Cartilage is firmer than other connective tissues.
The cells(chondrocytes) are sparse and lie embedded in matrix reinforced by collagen and elastic fibers.
There are 3 types :
1. Hyaline cartilage
2. Fibrocartilage.
3. Elastic fibrocartilage.
HYALINE CARTILAGE:
Hyaline cartilage is a smooth bluish white tissue.
The chondrocytes are arranged in small groups within cell nests and the matrix is solid and smooth.
Hyaline cartilage provides flexibility, support and smooth surfaces for movements at joints.
It is found on the ends of long bones that forms joints.
It forms the costal cartilages, which attach the ribs to the sternum.
It is found in the part of larynx, trachea and bronchi.
FIBRO CARTILAGE:
This consists of dense masses of white collagen fibers in a matrix similar to that of hyaline cartilage with the cells widely dispersed.
It is tough, slightly flexible, supporting tissue found: as pads between the bodies of vertebrae, the intervertebral discs.
Between the articulating surfaces of the bones of the knee joint , called semilunar cartilage.
On the rim of bony sockets of hips and shoulder joints, deepening the cavities without restricting movement.
ELASTIC FIBROCARTILAGE:
This flexible tissue consists of yellow elastic fibers lying in a solid matrix with chondrocytes lying between the fibers.
It provides support and maintain shape of eg: the pinna or the lobe of the ear, the epiglottis and the part of the tunica media of the blood vessel walls.
BONE:
Bone cells ( osteocytes)are surrounded by a matrix of collagen fibers strengthened by inorganic salts mainly calcium and phosphate.
This provides the bone with their characteristic strength and rigidity.
Bones also has considerable capacity for growth in the first two decades of life, and regeneration throughout life.
2 types of bones can be identified by naked eyes:
compact bone- solid or dense appearance.eg: femur ,tibia-long bones
spongy or cancellous bone- spongy or fine honeycomb appearance.eg: it is found in the ends of the long bones, ribs, skull





































Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for supporting me . ;I'll try my level best to give the accurate and updated knowledge in all the topics . please visit my YouTube channel named Nursing Abstract ; for viewing a brief explanation in both Tamil and English . see you again in my next post.