NERVOUS TISSUE:
TYPES OF TISSUES:
There are 4 main types of tissues each with subtypes .they are
1.EPITHELIAL TISSUE OR
EPITHELIUM.
2.CONNECTIVE TISSUE.
3.MUSCLE TISSUE.
4.NERVOUS TISSUE.
NERVOUS TISSUE:
It is a system that controls the body movements, sends and carries signals to and from the different parts of the body and has a role in controlling the bodily functions such as digestion.
2 types of tissue are found in the nervous system: excitable cells & non excitable cells.
Excitable cells –these are called neurons and they initiate, receive, conduct and transmit information.
Non excitable cells -also known as glial cells , these support the neurons.
NEURONS:
The cells are called which can transmit signals called nerve impulses, or action potentials
In neuron action potential is present which carry electrical impulses which can rise and fall quickly. the action potential can transmit signals from one neuron to the another.
Nervous tissue is formed of neurons which is also called as nerve cells and neuroglial cells.
CELLS IN NERVOUS TISSUE:
Four types of neuroglia cells found in the CNS are
Astrocytes,
Microglial cells,
Ependymal cells,
Oligodendrocytes.
Two types of neuroglia cells found in the PNS are satellite cells and Schwann cells.
GLIAL CELLS AND IT’S TYPES:
Neuroglia, or glial cells, are cells that support the neurons and supply them with the nutrients and get rid of the pathogens such as bacteria dead cells .
They also form an insulation between the neurons so that the electrical signals do not get crossed, and can also help in the formation of synaptic connections between the neurons. There are several types of neuroglia:
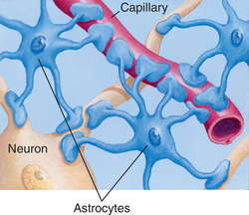
Astroglial cells are also called as astrocytes which are star-shaped cells. And they are found in the brain and the spinal cord. They provide nutrients to the neurons and maintain an ion balance, and remove the excess neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft which is not needed.
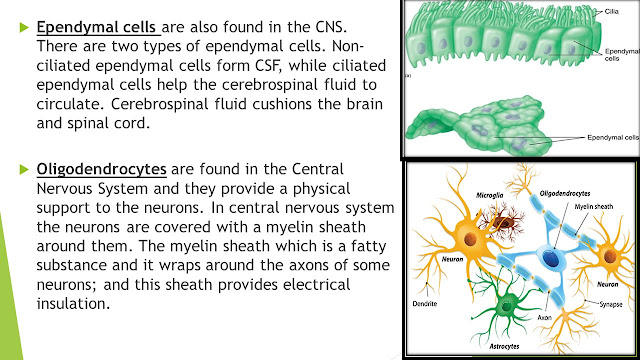
Ependymal cells are also found in the CNS. There are two types of ependymal cells. Non-ciliated ependymal cells form the CSF, while the ciliated ependymal cells help the cerebrospinal fluid to circulate. Cerebrospinal fluid cushions the brain and spinal cord.
Oligodendrocytes are found in the Central Nervous System and they provide a physical support to the neurons. In central nervous system the neurons are covered with a myelin sheath around them. The myelin sheath which is a fatty substance and it wraps around the axons of some neurons; and this sheath provides electrical insulation.
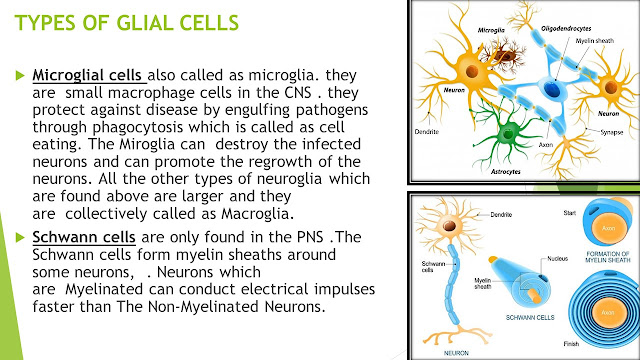
Microglial cells also called as microglia. they are small macrophage cells in the CNS . they protect against disease by engulfing pathogens through phagocytosis which is called as cell eating. The Miroglia can destroy the infected neurons and can promote the regrowth of the neurons. All the other types of neuroglia which are found above are larger and they are collectively called as Macroglia.
Schwann cells are only found in the PNS .The Schwann cells form myelin sheaths around some neurons, . Neurons which are Myelinated can conduct electrical impulses faster than The Non-Myelinated Neurons.
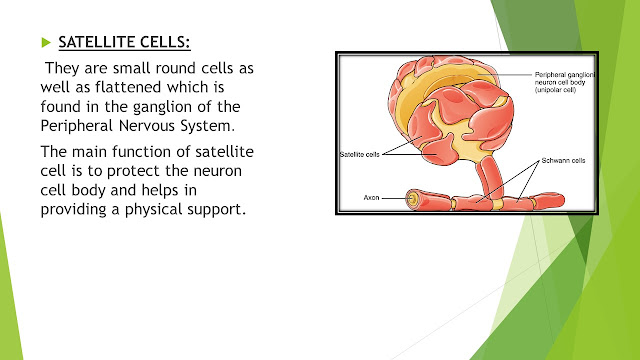
They are small round cells as well as flattened which is found in the ganglion of the Peripheral Nervous System.
The main function of satellite cell is to protect the neuron cell body and helps in providing a physical support.
















Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for supporting me . ;I'll try my level best to give the accurate and updated knowledge in all the topics . please visit my YouTube channel named Nursing Abstract ; for viewing a brief explanation in both Tamil and English . see you again in my next post.