Hello friends. This is a continuation of the AXIAL SKELETON . The Axial skeleton consists of the skull, vertebral column, the ribs and the sternum. In today's topic we are going to discuss about the " BONES OF THE CRANIUM" . I have made a video in both Tamil and English in the same topic .
English link :https://youtu.be/6f87pSK1qWs
Tamil link:https://youtu.be/GTXqCsjQ8Us
AXIAL SKELETON:
The Axial skeleton consists of the
SKULL:
The skull is resting on the upper end of the spinal column
Its bony structures are divided into two parts:
- The cranium
- The Face.
SINUSES:
Sinuses contain air .They are present within the sphenoid, ethmoid, maxillary and frontal bones.
Sinuses are lined with ciliated mucous membrane and they communicate with the nasal cavity .
They give resonance to the voice and the sinuses reduces the load of the skull, which makes it easier to hold .
CRANIUM:
The cranium is made up of flat and irregular bones. It’s function is to protects the brain.
It has a base on which the brain rests and a vault which covers and surrounds the brain.
The skull bones has a outer layer which is made up of dura matter and inner layer is lined up with periosteum.
In mature skull the joints between the bones are immovable {can’t move} these joints are called as sutures.
The bones have perforations or holes which is called as foramina and fissures which a deep groove through which nerves, blood and lymph vessels pass.
BONES OF CRANIUM:
The bones of the cranium are
• 1 frontal bone
• 2 parietal bones
• 2 temporal bones
• 1 occipital bone
• 1 sphenoid bone
• 1 ethmoid bone
FRONTAL BONE:
It is also called as the forehead bone.
It forms the part of the orbital cavities( i.e. eye sockets) and the prominent ridges which are above the eyes and the supraorbital margins.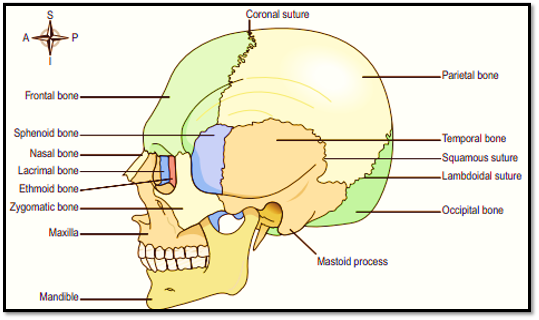
Just above the supraorbital margins within the bone there are two air-filled cavities i.e. the sinuses which are lined up with ciliated mucous membrane and it opens into the nasal cavity.
The frontal and parietal bones joins together and form the coronal suture.
The frontal bone consists of frontal suture divides it into right and left halves present in newborn and children closes by three – nine months of age .
PARIETAL BONES:
The Parietal bones forms the edges and roof of the skull.
They articulate with each other at the sagittal suture which make the parietal bone into right and left half, with the frontal bone at the coronal suture, the occipital bone at the lambdoidal suture and the temporal bones at the squamous sutures.
The inner surface is concave and it has a groove to accommodate the brain and blood vessels.
TEMPORAL BONE:
These bones lie on each side of the head and form squamous sutures with the bones such as parietal, occipital, sphenoid and zygomatic bones.
The squamous part which is a thin fan-shaped area which articulates with the parietal bone.
The zygomatic process which articulates with the zygomatic bone and it forms the zygomatic arch (cheekbone).
The mastoid part consists of the mastoid process, a thickened region which is easily felt behind the ear.
The Sphenoid sinuses that communicate with the middle ear and are lined with squamous epithelium.
The temporal bone articulates with the mandible and forms the temporomandibular joint, which is the only movable joint of the skull
The external acoustic meatus (auditory canal), which is a bony canal runs from outer to inner ear .
The styloid process which projects from the lower process of the temporal bone which supports the hyoid bone and the muscles which are associated with the tongue and pharynx.
OCCIPITAL BONE:
This bone forms the back of the head and the base of the skull.
It forms the lambdoidal sutures with the parietal, temporal and sphenoid bones.
The inner surface is deeply concave and it is occupied by the occipital lobes of the cerebrum and the cerebellum.
The occiput has two articular condyles that forms the condyloid joints with the first bone of the vertebral column called as the atlas.
This joint permits the nodding movements of the head.
Between the condyles there is a hole called as the foramen magnum (meaning ‘large hole’) through which the spinal cord passes into the cranial cavity.
SPHENOID BONE:
The Sphenoid bone occupies the middle portion of the base of the skull and it articulates with the bones such as the occipital, temporal, parietal and frontal bones .
It links the cranial and facial bones, and cross-braces { supports or hold} the skull.
In the middle of the bone is a little saddle-shaped depression called as the Hypophyseal fossa in which the pituitary gland rests.
The body of the bone contains sphenoid sinuses lined with ciliated mucous membrane with openings into the nasal cavity.
The optic nerves pass through the optic foramina which connects to the brain.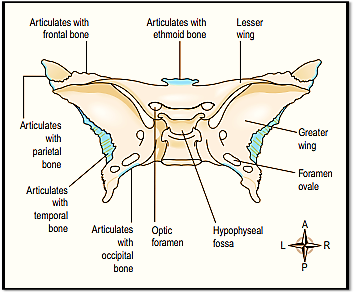
ETHMOID BONE:
The ethmoid bone is situated in the anterior part of the base of the skull and it helps to form the orbital cavity, the nasal septum and the lateral walls of the nasal cavity.
On each side there are two projections into the nasal cavity, the superior and middle .
It is a very delicate bone containing ethmoid sinuses which is lined with ciliated epithelium and it opens into the nasal cavity.
The horizontal flattened part i.e. the cribriform plate, forms the roof of the nasal cavity and it has numerous small foramina { holes} through which nerve fibres of the olfactory nerve (sense of smell) pass upward from the nasal cavity to the brain
These are the slides which I'm using in my videos
.






















Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for supporting me . ;I'll try my level best to give the accurate and updated knowledge in all the topics . please visit my YouTube channel named Nursing Abstract ; for viewing a brief explanation in both Tamil and English . see you again in my next post.