Hello guys.. My greetings to one and all. So far we are discussing about the basic concepts of human body. Today's topic is one of the important topic. i.e. "THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS". we'll be coming across the thyroid, pancreas, the ovaries in our day to day life. But how many of you know that they are associated with glands and they produce hormones?... If your not aware today these slides will help you to know the basic concepts of glands.
I'm also running an YouTube channel named "NURSING ABSTRACT". Where you can find explanation of these slides in both Tamil and English. If you have any suggestions kindly post in the comments section below.
Channel link:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCZrabu-CtMa5AEexu1j2GNw
English video:https://youtu.be/VlWv5e89Nv8
Tamil video:https://youtu.be/zysI2bc1CA0
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
GLANDS:
Glands are organs which are very important and it is located throughout your body .
We have hundreds of small bean shaped glands all over the body .
Glands are group of epithelial cells.
They produce and release specialized secretions that perform certain functions.
There are organs that contain endocrine tissue and act as glands.
TYPES OF GLANDS:
Glands are classified into 2 types :Endocrine & Exocrine glands.
ENDOCRINE GLANDS:
Endocrine glands (ductless glands) are part of your endocrine system. They produce hormones and it is released in your bloodstream. These hormones control a number of important functions in your body, such as:
your growth and development
Metabolism
Mood
reproduction.
Your endocrine glands include:
1. adrenal glands
2.pituitary gland
3.hypothalamus
4.thyroid
5.pineal gland
There are organs that contain endocrine tissue and act as glands. These include the:
6.pancreas
7.kidneys
8.ovaries
9.testes.
Adrenal glands :
Hormone : Aldosterone
Regulates the salt water balance, and maintains BP.
Adrenal glands:
Hormone: Corticosteroid
Controls key functions within the body; acts as an anti-inflammatory; maintains blood glucose levels, blood pressure, and muscle strength; regulates salt and water balance.
Adrenal glands:
Hormone: Epinephrine
Increases heart rate, oxygen intake, and blood flow.
Adrenal glands:
Hormone: Norepinephrine
Maintains blood pressure
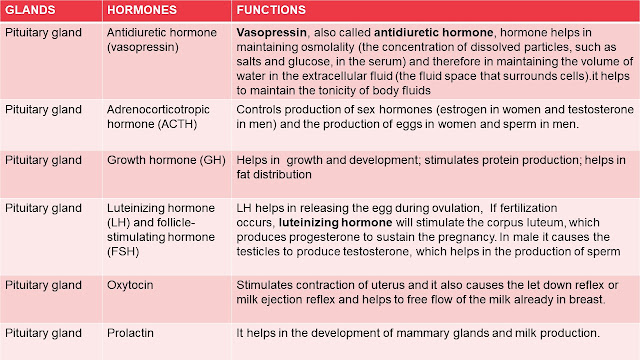
Pituitary gland:
Hormone: Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Stimulates the production and secretion of thyroid hormones.
Pituitary gland:
Hormone: Antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin)
Vasopressin, also called ADH, hormone helps in maintaining osmolality (the concentration of dissolved particles, like salts and glucose, within the serum) and thus in maintaining the quantity of water in the extracellular fluid (the fluid space that surrounds cells).it helps to maintain the tonicity of body fluids
Pituitary gland:
Hormone: Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Controls production of sex hormones (estrogen in women and testosterone in men) and therefore the production of eggs in women and sperm in men.
Pituitary gland:
Hormone: Growth hormone (GH)
It helps in the growth and development; stimulates protein production; helps in fat distribution.
Pituitary gland:
Hormone: Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
LH helps in releasing the egg during ovulation, If fertilization occurs, luteinizing hormone will stimulate the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone to sustain the pregnancy. In male it causes the testicles to produce testosterone, which helps in the production of sperm.
Pituitary gland:
Hormone: Oxytocin
Stimulates contraction of uterus and it causes the let down reflex or milk ejection reflex and helps to free flow of the milk already in breast.
Pituitary gland:
Hormone: Prolactin
It helps in the development of mammary glands and milk production.
Thymus:
Hormone: Thymosin
Helps to develop the T Cells and helps in production of GH {Growth hormones}.
Thyroid gland:
Hormone: Thyroid hormone
Controls metabolism; also Helps in growth, maturation, nervous system activity.
Parathyroid glands:
Hormone: Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Most important regulator of blood calcium levels
Ovaries:
Hormone: Estrogen
Develop and maintain the female reproductive organs. Controls the growth of uterine lining during menstrual cycle, causes breast changes in teenagers.
Ovaries:
Hormone: Progesterone
Stimulates layers of the uterus for fertilization; prepares the breasts for milk production
Testes (testicles):
Hormone: Testosterone
Develop and maintain male sexual characteristics and maturation
Kidneys:
Hormone: Renin and angiotensin
Regulates the blood pressure and electrolyte balance and also by regulating aldosterone production from the adrenal glands
Kidneys:
Hormone: Erythropoietin
It helps in the red blood cell (RBC) production
Pancreas:
Hormone: Insulin
Lowers blood glucose levels; stimulates metabolism of glucose, protein, and fat
Pancreas:
Hormone: Glucagon
The pancreas releases glucagon when the quantity of glucose within the bloodstream is just too low. Glucagon causes the liver to interact in glycogenolysis, converting stored glycogen into glucose, which is released into the bloodstream. High blood-glucose levels, on the opposite hand, stimulate the discharge of insulin
Pineal gland:
Hormone: Melatonin
Releases melatonin during night hours to assist with sleep
Hypothalamus:
Hormone: Corticotrophin releasing hormone (CRH)
Regulates Adreno corticotropin hormone{ACTH} release in the pituitary gland
Hypothalamus:
Hormone: Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH)
Regulates growth hormone release in the pituitary gland
Hypothalamus:
Hormone: Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
Regulates LH/FSH production in the pituitary gland
Hypothalamus:
Hormone: Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH)
Regulates thyroid stimulating hormone release within the pituitary .
Thymus:
Hormone: Thymosin
Helps to develop the T Cells and helps in production of GH {Growth hormones}.
These are the slides which I'm using in my videos.











Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for supporting me . ;I'll try my level best to give the accurate and updated knowledge in all the topics . please visit my YouTube channel named Nursing Abstract ; for viewing a brief explanation in both Tamil and English . see you again in my next post.