Hello friends .. In today's topic we are going to discuss about " THE CARDIAC CYCLE". If you have any doubts please post in the comments section below . I have also made the content in a video in Tamil and English .I'm giving the link below..
YOU TUBE CHANNEL LINK:https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCZrabu-CtMa5AEexu1j2GNw
ENGLISH VIDEO : https://youtu.be/SkqabJmffEc
TAMIL VIDEO:https://youtu.be/DSzgU4vaVwc
INTRODUCTION:
The healthy adult heart beats at a rate of 60–80 beats per minute at rest.
Stages of the cardiac cycle:
• In Atrial systole – contraction of the atria takes place.
• In ventricular systole – contraction of the ventricles takes place.
•In complete cardiac diastole – relaxation of the atria and ventricles takes place.
During each heartbeat also called as cardiac cycle the heart contracts (systole) and relaxes (diastole).
Taking 74 beats per minute as an example, each cycle lasts about 0.8 of a second.
ATRIAL SYSTOLE:
The superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava transport deoxygenated blood into the right atrium and the four pulmonary veins bring oxygenated blood into the left atrium at the same time .
The atrioventricular valves are open and blood flows passively through without any effort to the ventricles.
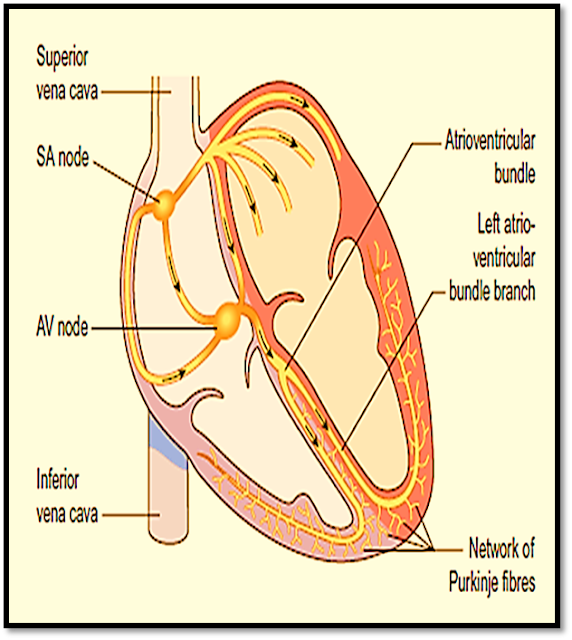
The SA node which is the pace maker of the heart triggers a wave of contraction that spreads through the myocardium of both atria, emptying the blood from the atria and completing ventricular filling (atrial systole 0.1s).
When the electrical impulse reaches the AV node the transmission of waves are slowed down which delays the atrioventricular transmission.
VENTRICULAR SYSTOLE:
This delay causes the mechanical result of atrial stimulation, atrial contraction to lag behind the electrical activity to a fraction of a second.
This delay allows the atria to finish emptying into the ventricles before the ventricles begin to contract.
After this delay, the AV node triggers its own electrical impulse and then quickly spreads to the ventricular muscle via the AV bundle, the bundle branches and Purkinje fibers.
This results in a wave of contraction which moves upwards from the apex of the heart across the walls of both ventricles pumping the blood into the pulmonary artery and the aorta (ventricular systole 0.3 s).
COMPLETE CARDIAC DIASTOLE:
The high pressure which generates during ventricular contraction forces the atrioventricular valves to close which prevents the backflow of blood into the atria.
After contraction of the ventricles there is complete cardiac diastole for a period of 0.4 seconds, where the atria and ventricles are relaxed.
In this time the myocardium recovers and it will be ready for the next heartbeat in mean while the atria refill and will be ready for the next cycle .
The valves of the heart and the great vessels i.e. The Aorta and Pulmonary Trunk open and close according to the pressure within the chambers of the heart.
During atrial filling and systole the AV valves are open and the ventricular muscle is relaxed.
PRESSURE CHANGE IN THE ATRIUM AND VENTRICLES:
When the ventricles contract there is a rapid increase in the pressure in the ventricles, and when the pressure rises above atrial pressure the atrioventricular valves close and the pulmonary and aorta open and blood flows into these vessels.
When the ventricles relax and the pressure within the ventricles falls, the reverse process occurs.
When the pulmonary and aorta valves close, then the atrioventricular valves open . Then the cycle begins again.
This process of opening and closing of the valves ensures that the blood flows in only one direction.
HEART SOUNDS:
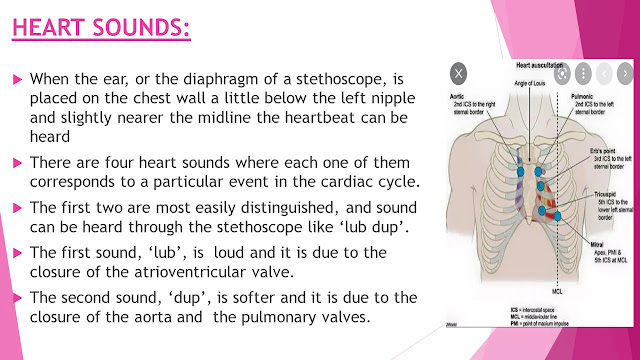
When the ear, or the diaphragm of a stethoscope, is placed on the chest wall a little below the left nipple and slightly nearer the midline the heartbeat can be heard
There are four heart sounds where each one of them corresponds to a particular event in the cardiac cycle.
 The first two are most easily distinguished, and sound can be heard through the stethoscope like ‘lub dup’.
The first two are most easily distinguished, and sound can be heard through the stethoscope like ‘lub dup’.
The first sound, ‘lub’, is loud and it is due to the closure of the atrioventricular valve.
The second sound, ‘dup’, is softer and it is due to the closure of the aorta and the pulmonary valves.
These are the slides which I'm using in the videos.









.jpg)

Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for supporting me . ;I'll try my level best to give the accurate and updated knowledge in all the topics . please visit my YouTube channel named Nursing Abstract ; for viewing a brief explanation in both Tamil and English . see you again in my next post.